Bringing Science to Justice: Impact of the Expert Consensus Statement on the Science of HIV in the context of criminal law over the past five years (Poster)
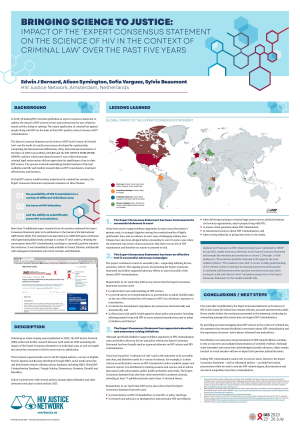
Research findings on the five-year impact of the ‘Expert Consensus Statement on the Science of HIV in the Context of Criminal Law’, presented at the International AIDS Conference (IAS 2023). The research examined the impact of the Expert Consensus Statement on individual cases as well as broader law and policy outcomes in the five years since its publication and found that the statement remains relevant, accurate and extremely useful. Newer studies bolster the conclusions presented in the statement, reinforcing its overarching message that science does not support HIV criminalisation.
Change the world: A toolkit for citizen journalists
This training manual helps lay the foundation for civil society advocates to become citizen journalists. It brings together journalism skills and advocacy goals to help Key Correspondents share their perspectives and experience with decision makers and wider audiences to influence the discourse around HIV and related issues. The manual introduces the basic components of journalism; so correspondents can write their stories with accuracy and using a journalistic approach to improve the potential of being published in mainstream media. It is a ‘how to’ guide for individual study.
How reliable is an undetectable viral load
Considers the reliability of viral load as a condition preventing HIV transmission. Found reliability is high with compliance taking medication the most important factor predicting reliability.
Keeping Confidence: HIV and the criminal law from service provider perspectives
Based on discussions with 75 service providers, this study found that criminalisation has influenced, and sometimes disrupted provision of HIV services, creating ambivalence and concern among many providers about their new role as providers of legal information. Service providers’ approach were influenced by their personal views on shared responsibility for health, concerns about professional liability and their degree of trust in non-coercive approaches to managing public health.
Controlling Sex in the Name of “Public Health”: Social Control and Michigan HIV Law
Found that local health officials’ interpretation of ‘health threat’ and understanding of the law varied. Indicates how public health institutions themselves may contribute to and facilitate enforcement of Michigan’s problematic HIV disclosure law. Shows that stigma and fear often drive community members to police HIV-positive neighbours’ disclosure practices.
Criminal Law and Public Health Practice: Are the Canadian HIV Disclosure Laws an Effective HIV Prevention Strategy?
Considers the effect of HIV criminalisation on HIV prevention, finding that although criminal laws might prevent HIV transmission in a few isolated cases, it is unlikely they would influence overall population-level rates of HIV transmission. Some evidence suggests these laws could exacerbate HIV transmission.